Paramecium week on the radio Ö1: Paramecium in focus with Dr. Bettina Sonntag (in German):
Read More08
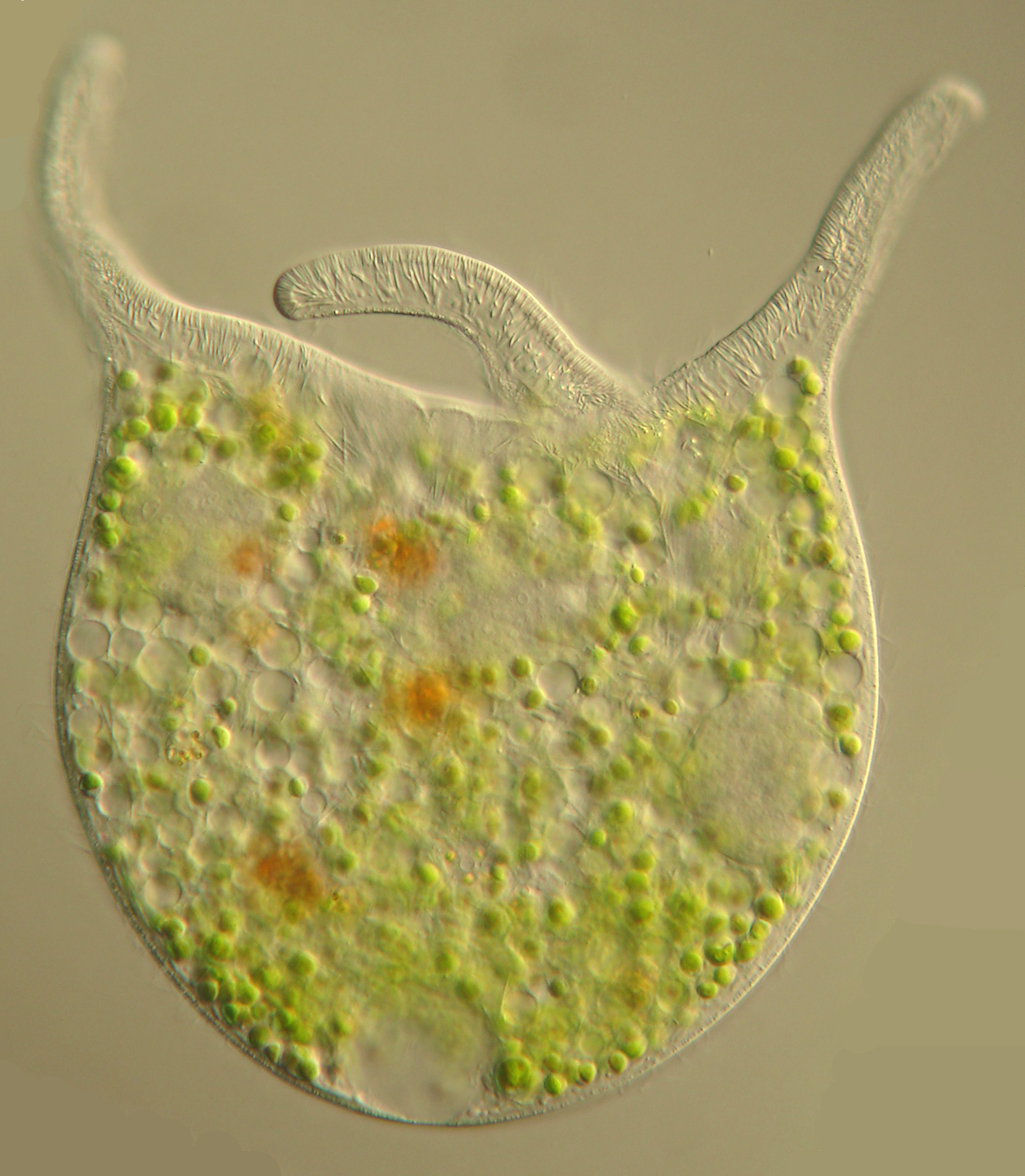
Teuthophrys trisulca trisulca
Teuthophrys trisulca trisulca lives in a mutualistic relationship with green algal symbionts. This relatively large – up to 0.3 mm – ciliate catches small multicellular organisms (e.g., rotifers) as food. Teuthophrys trisulca trisulca can be found in lake plankton.
Read More29
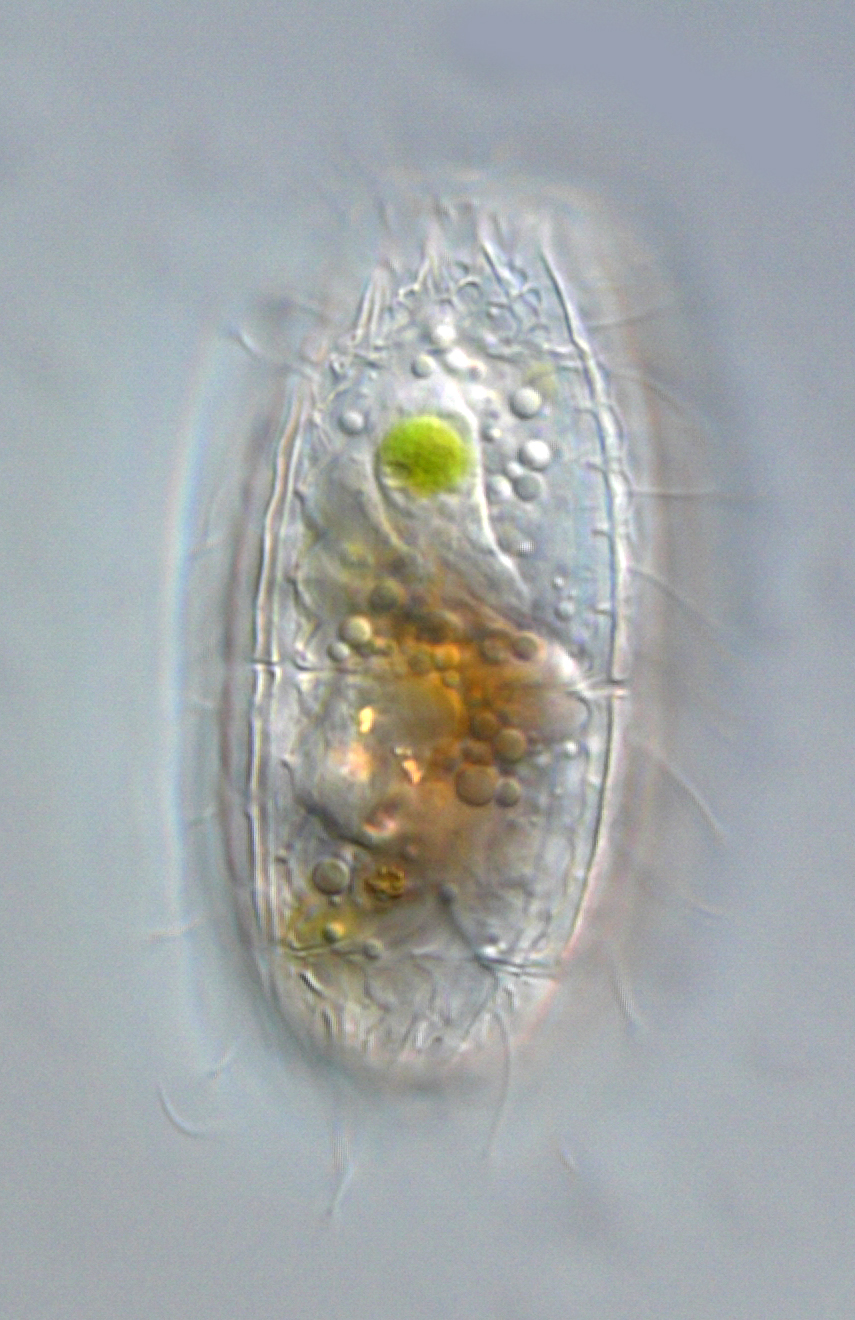
Coleps hirtus hirtus
Coleps hirtus is a heterotrophic ciliate species that feeds directly on other microbes including bacteria and other protists. To reveal the characteristic pretzel-shaped ‘windows’ of the calcified armor, this individual found in Lake Mondsee (Austria) was strongly squeezed.
Read More27
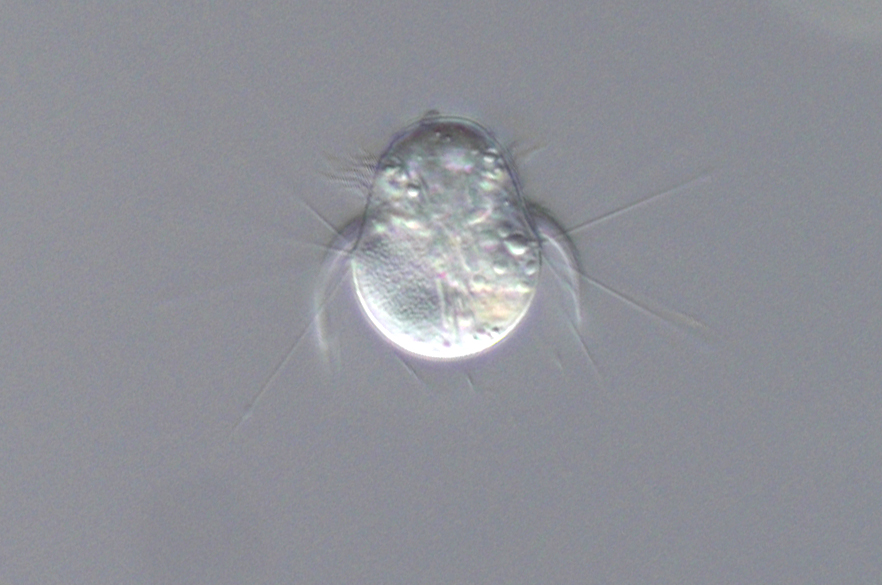
Rhabdoaskenasia minima
Rhabdoaskenasia minima is a small (30 x 20 µm) planktonic ciliate commonly found in lakes. This ciliate contains three characteristic ciliary girdles in the anterior half of the cell: one having relatively short cilia, another one with longer cilia that are typically bent posterior and a third girdle with long bristles that faciliate floating in […]
Read More27
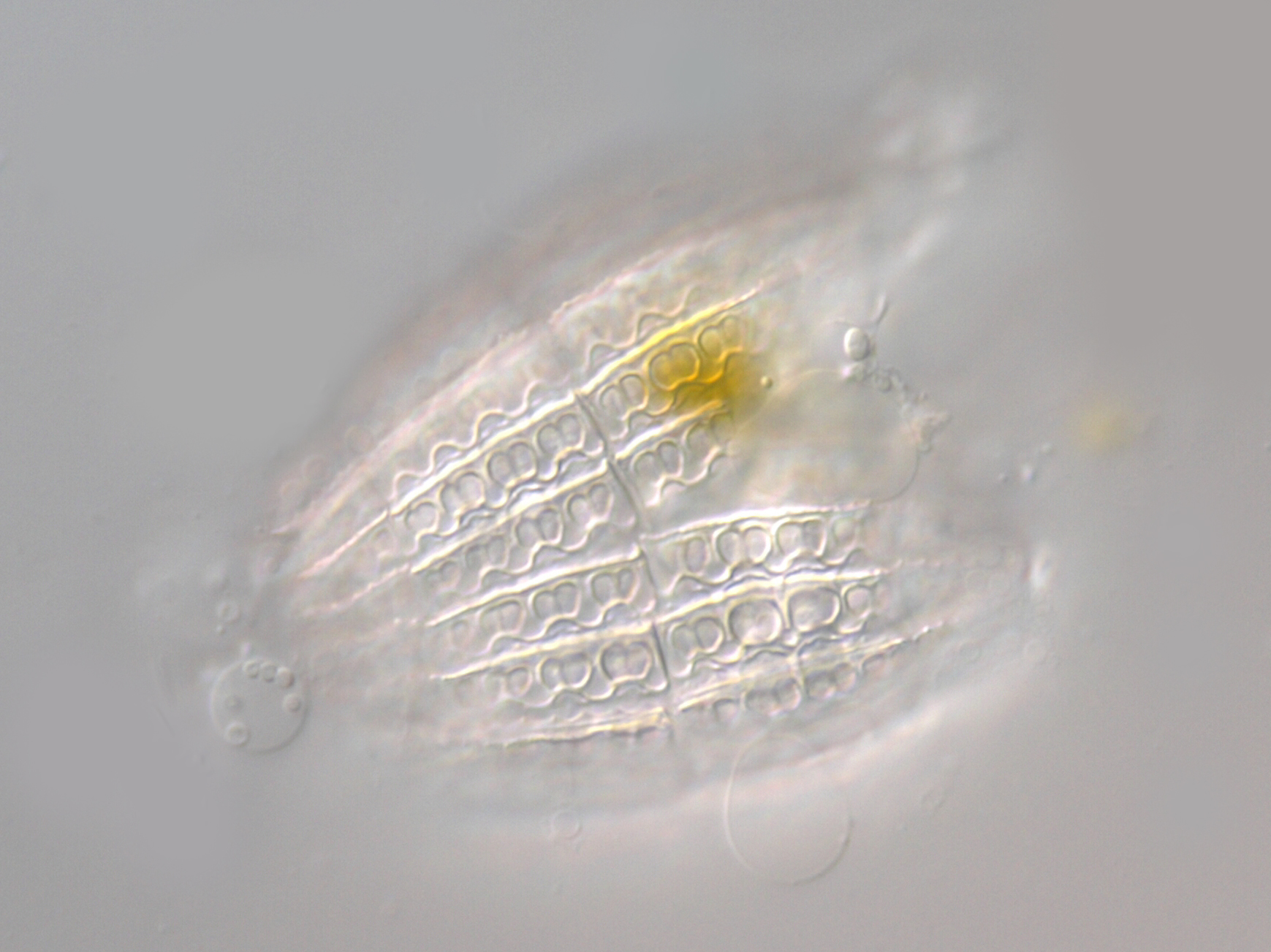
Coleps nolandi
Coleps nolandi is a ciliate covered by calcified armored plates. The main plates bear species-specific ‘windows’ which have a reniform shape in C. nolandi (see picture below). The ciliate is found in benthic and pelagic freshwater habitats and feeds on algae, other ciliates and organic debris.
Read More05
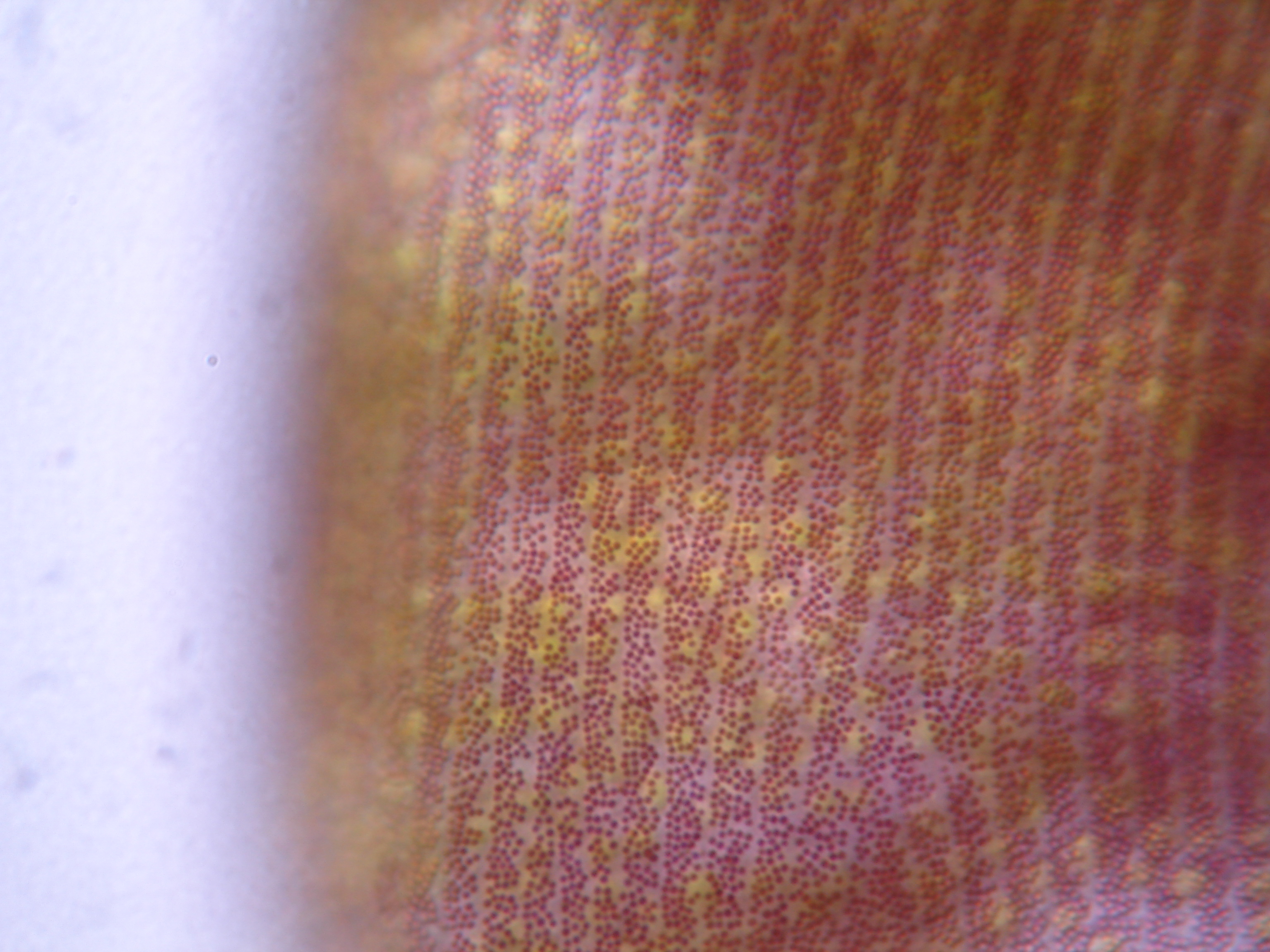
Stentor amethystinus
Stentor amethystinus is a trumpet-shaped ciliate with a violet to purple appearance. The ciliate is almost 1 mm long and common in lake and pond plankton. Inside the ciliate unicellular algae (the globular green cells) live in symbiosis with S. amethystinus. Stentor is the Unicellular Eukaryote of the Year 2014. This population was sampled by Samuel […]
Read More13
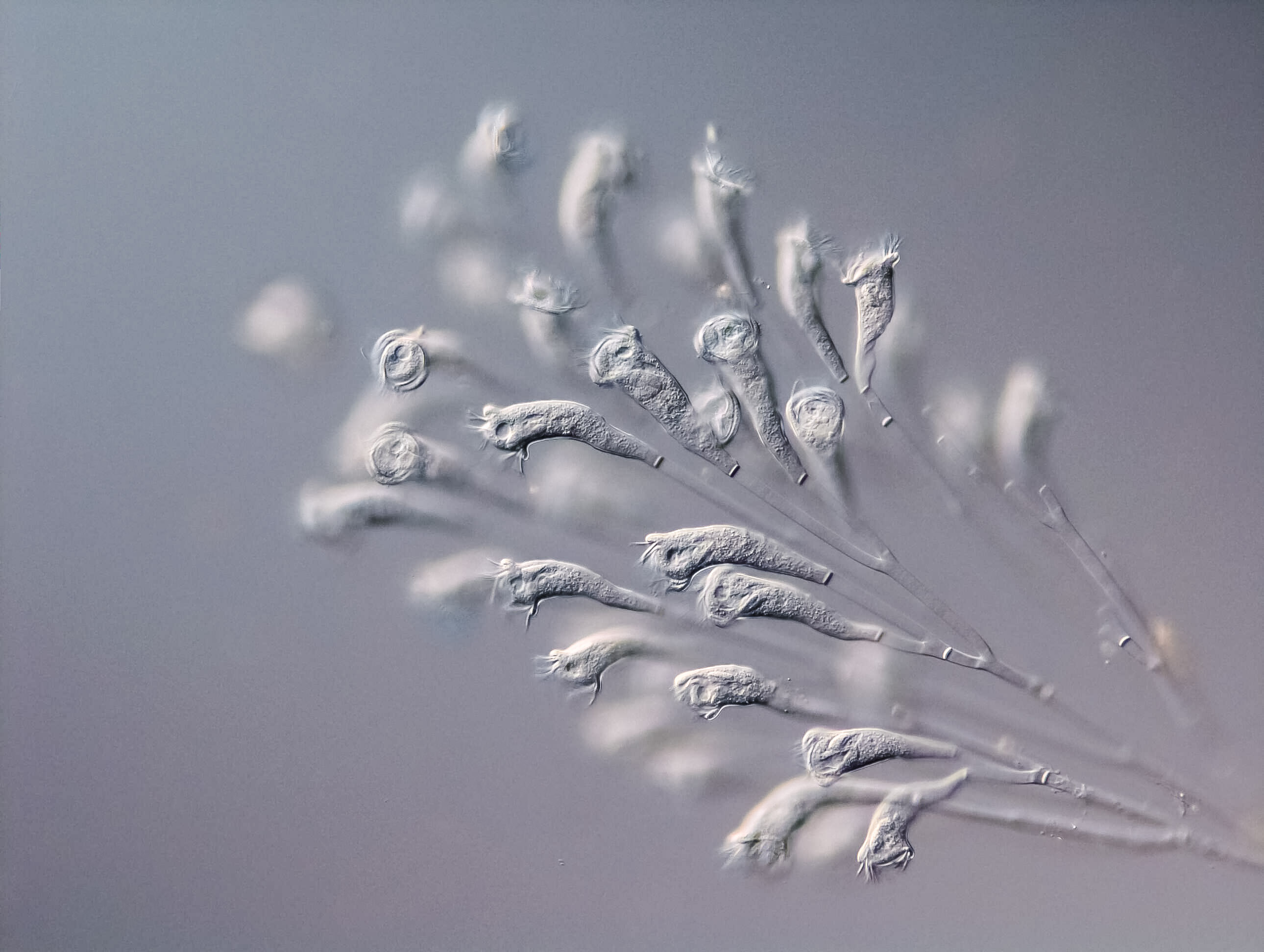

Epistylis procumbens
Epistylis procumbens (Video) is a colony-forming ciliate thriving in lake plankton. Individuals feed on bacteria and smaller other protists. Contribution from Harald Bernhard, Philipp Stüber and Daniel Feldbacher who investigated the ciliates from Mondsee during a practical summer course.
Read More06
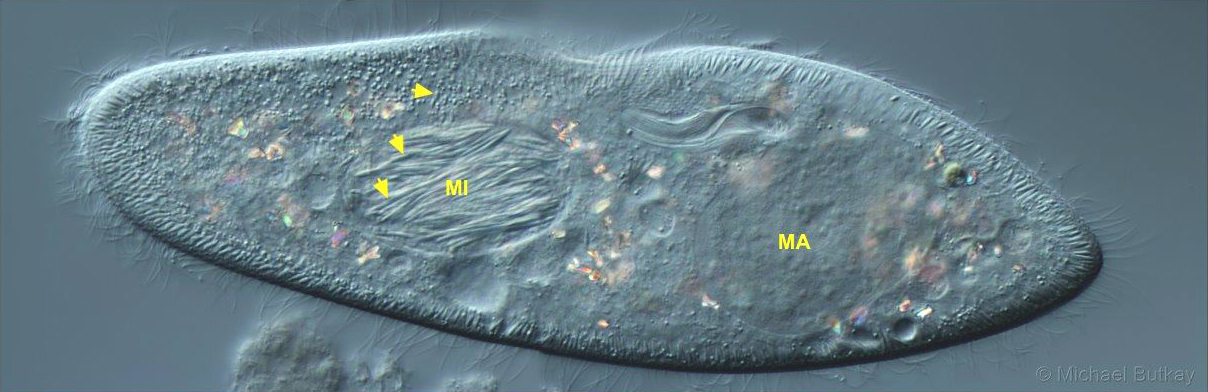
Paramecium caudatum
Bacteria of the genus Holospora (H. elegans, arrows) colonize the micronucleus (MI) of the ciliate Paramecium caudatum (‘endonuclear symbionts’). The bacteria actively invade the ciliate and the nucleus and are also given to the daughter cell during division. Some bacteria are also released to the environment to infect new hosts. The macronucleus is also visible […]
Read More12
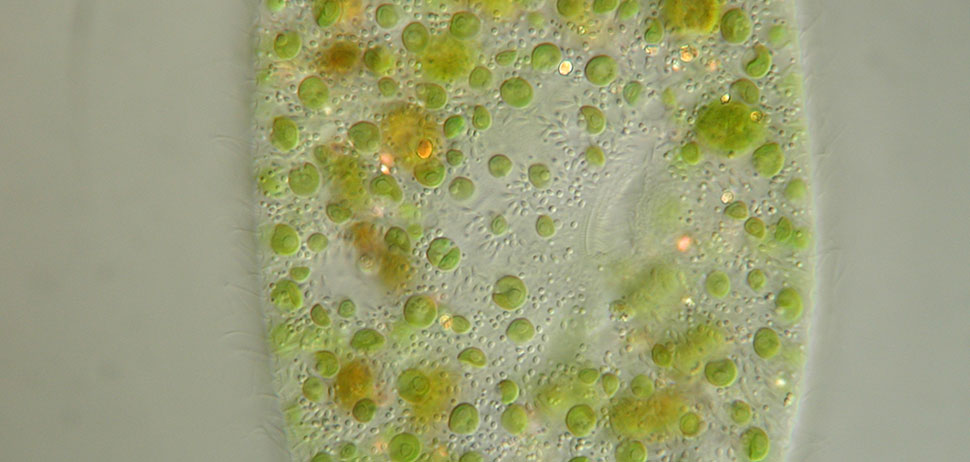
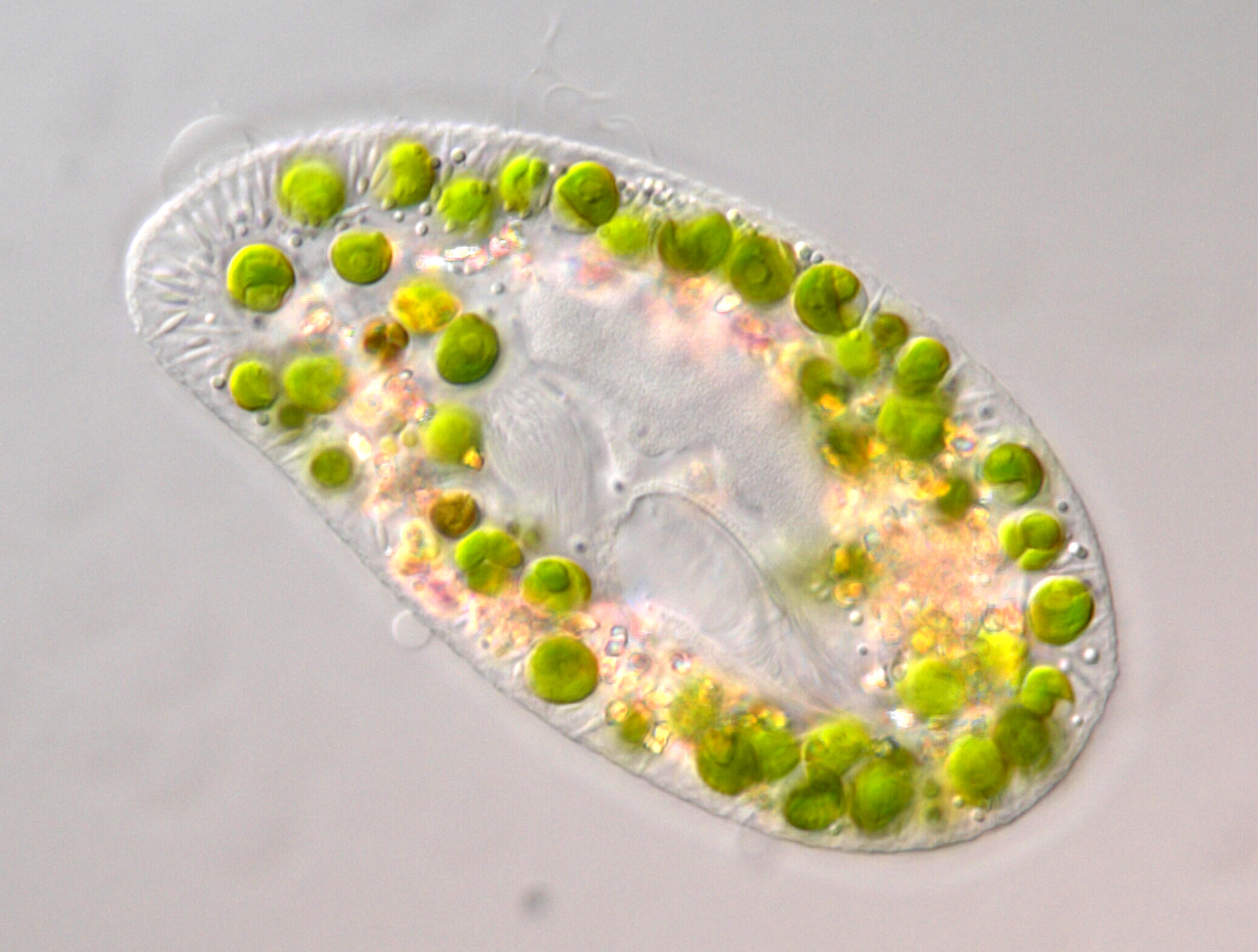
Paramecium bursaria
Paramecium bursaria (Video) is a model ciliate in protist science that lives in symbiosis with algae (green). Here, we see the characteristic two contractile vacuoles with the collecting channels, the cell mouth (slit-like depression with many moving cilia in the middle of the cell) and the macronucleus (appears ellipsoidal in grey).
Read More12
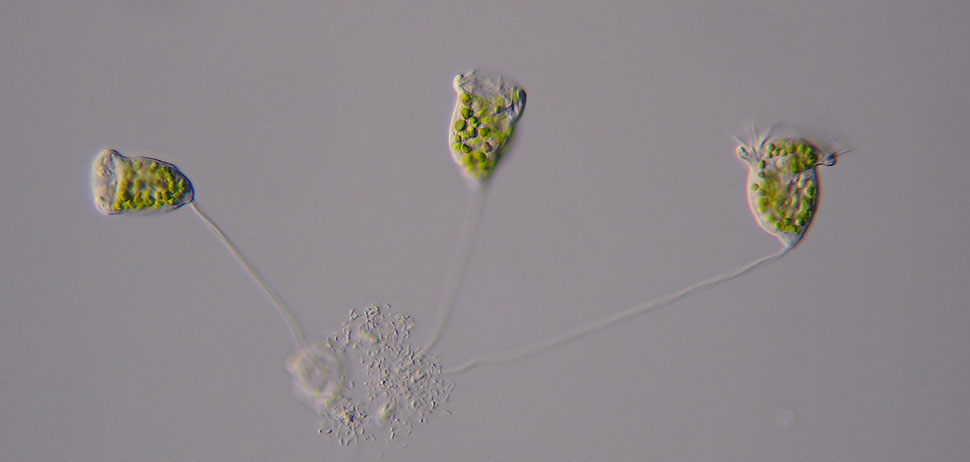
Vorticella chlorellata
Individuals of Vorticella chlorellata posess a stalk with which they are attached to other plankton or debris. In this combination they are too large to be ingested by predators. The symbiotic algae (green) provide photosynthetic products to the ciliates and are able to synthesize UV sunscreen compounds (MAAs).
Read More

02